Acne is one of the most common skin conditions worldwide, affecting people of all ages especially teens and young adults. Though often seen as a cosmetic issue, acne can have a deep emotional and psychological impact, affecting self-esteem and confidence.
WHAT IS ACNE?
Acne is a skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil (sebum) and dead skin cells. This leads to whiteheads, blackheads, pimples, and in more severe cases, painful cysts or nodules.
COMMON CAUSES OF ACNE

1. HORMONAL CHANGES
Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or due to conditions like PCOS can increase oil production in the skin.
2. EXCESS OIL PRODUCTION
Overactive sebaceous glands produce too much sebum, leading to clogged pores.
3. BACTERIA
The bacterium Cutibacterium acnes (C. acnes) can multiply in clogged pores, causing inflammation.
4. DIET
Some studies suggest a link between acne and high glycemic index foods, dairy, and processed foods.
5. STRESS
Stress doesn’t directly cause acne but can worsen existing breakouts.
6. GENETICS
A family history of acne increases your risk of developing it.
TYPES OF ACNE
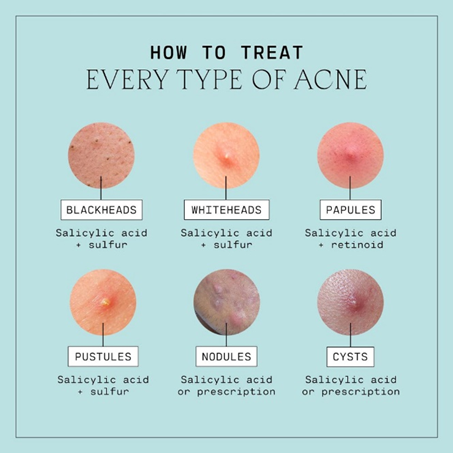
– Whiteheads – Closed clogged pores.
– Blackheads – Open clogged pores that turn dark.
– Papules – Small, red, tender bumps.
– Pustules – Pimples with pus at their tips.
– Nodules – Large, painful lumps under the skin.
– Cysts – Deep, pus-filled infections that can cause scars.
TREATMENT OPTIONS

1. TOPICAL TREATMENTS
– Benzoyl Peroxide: Kills bacteria and dries excess oil.
– Salicylic Acid: Helps unclog pores.
– Retinoids: Promotes skin turnover and prevents clogged pores.
– Antibiotic creams: Reduce bacteria and inflammation.
2. ORAL MEDICATIONS
– Antibiotics: Control bacteria and reduce inflammation.
– Birth control pills: Regulate hormones in women.
– Isotretinoin (for severe cases): A powerful vitamin A derivative.
3. NATURAL REMEDIES (WITH CAUTIONS)
– Tea tree oil, green tea extract, and aloe vera may help mild acne, but results vary.
4. LIFESTYLE AND SKINCARE
– Use non-comedogenic products.
– Wash your face gently twice a day.
– Avoid over-scrubbing or harsh treatments.
– Keep hair and hands away from your face.
WHEN TO SEE A DERMATOLOGIST
If over-the-counter treatments don’t work or if acne is causing scars, pain, or emotional distress, consult a dermatologist for personalized care.
Acne is common, but it’s treatable. Understanding its causes and options can help manage breakouts effectively. Remember, clear skin is a journey, not a race, and you deserve support and care at every step.

